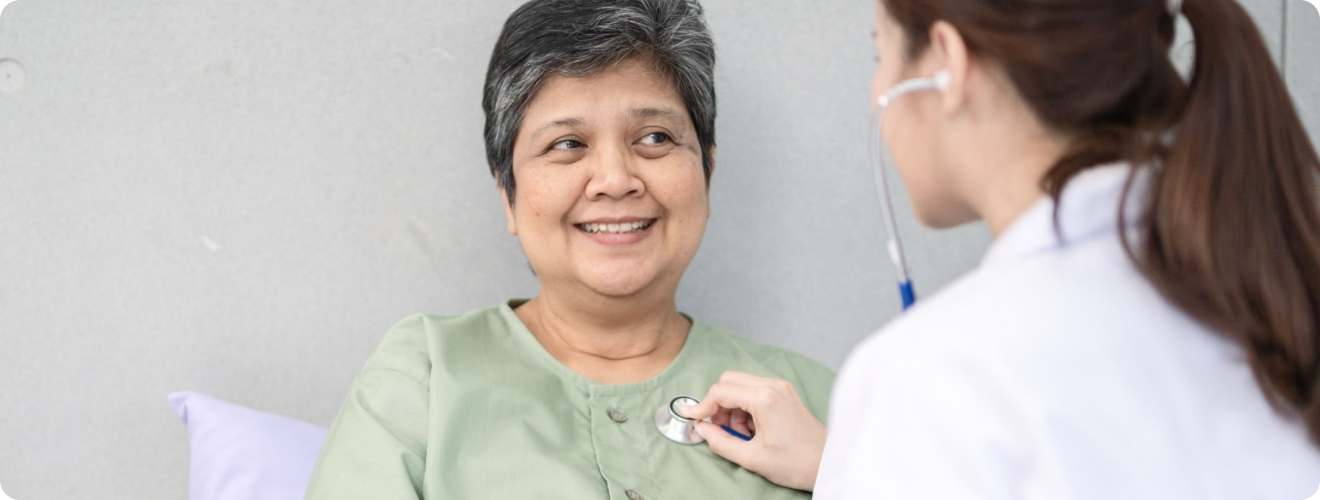



Lung health is a topic that affects every one of us, whether we realise it or not. Breathing is something we often take for granted, and only put importance on when we face issues with our respiratory system. Any problems in our respiratory system encounters can have a significant impact on our overall well-being.
In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the world of lung health, exploring the causes, symptoms, and treatment of respiratory disorders.
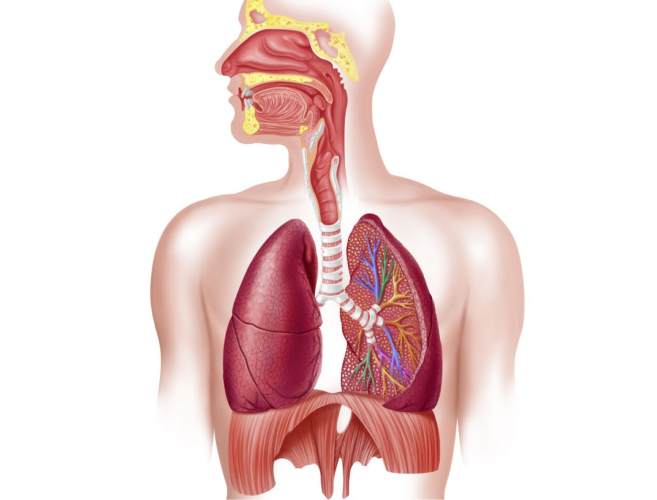
The respiratory system is a complex network of organs and tissues responsible for the intake of oxygen and the removal of carbon dioxide from the body. Understanding how this system functions is crucial in diagnosing and treating respiratory diseases, as well as optimising lung function.
The process begins with inhalation, whereby air enters through the nose or mouth, travels down the trachea, and branches into smaller tubes called bronchi. These bronchi further divide into even smaller airways known as bronchioles, which eventually lead to tiny air sacs called alveoli. It is within these alveoli that gases are exchanged – oxygen diffuses from the lungs into the bloodstream while carbon dioxide is eliminated.
Additionally, the respiratory system plays a role in regulating pH levels through its control over breathing rate and depth. In professional contexts, such knowledge allows healthcare practitioners to accurately assess respiratory health and provide appropriate interventions when necessary.
Maintaining good lung health involves more than just genetics and medical care; lifestyle and environmental factors play a significant role. By making conscious choices and minimising exposure to harmful elements, you can promote better lung health.
Here are key lifestyle and environmental factors that influence lung health:
Recognising the signs and symptoms of respiratory disorders is important for early diagnosis and intervention. Many respiratory conditions share common symptoms, so it is essential to pay attention to any changes in your breathing or overall health.
The typical signs and symptoms associated with respiratory disorders include:
The diagnosis and screening of respiratory disorders involve a combination of medical history assessments, physical examinations, and various diagnostic tests. Identifying the specific respiratory condition is crucial for effective treatment and management. Here are the common methods and procedures used for the diagnosis and screening of respiratory disorders:
The treatment and management of respiratory disorders depend on the specific condition diagnosed, its severity, and individual patient factors. While treatment plans vary based on a person’s health condition, here are some common approaches and strategies used to manage respiratory disorders:
Inhalers and nebulisers deliver medications directly to the lungs and are commonly used for asthma and COPD management.
Oxygen therapy may be prescribed for individuals with low blood oxygen levels (hypoxaemia). Portable oxygen concentrators or oxygen tanks can be used to improve oxygen saturation.
Pulmonary rehabilitation programmes offer a structured approach to improve lung function, physical fitness, and overall quality of life for individuals with chronic lung diseases.
Influenza and pneumonia vaccines are recommended for individuals with respiratory disorders to prevent respiratory infections and complications.
Surgical interventions may be necessary in some cases, such as lung cancer resection, lung transplantation, or procedures to remove lung abscesses.
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) or Bilevel Positive Airway Pressure (BiPAP) machines are used to treat sleep apnoea by delivering pressurised air to keep airways open during sleep.
Chest physiotherapy and devices such as flutter valves or positive expiratory pressure (PEP) devices can assist in clearing mucus from the airways.
Avoiding allergens or irritants that trigger symptoms, such as dust mites, pollen, or pollutants, is essential.
While traditional medical treatments and lifestyle modifications are essential for maintaining lung health, some supportive therapies and alternative treatments may complement conventional care. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any alternative treatments, especially if you have a respiratory condition.
Here are some supportive therapies and alternative treatments that individuals may consider:

Maintaining optimal lung health is a very important component of our overall well-being. Gaining a comprehensive understanding of the underlying causes, identifying symptoms, and exploring available treatment options for respiratory disorders empower us to proactively manage our lung health.
By making informed choices and promptly seeking medical attention when necessary, we can all experience a greater sense of ease in our breathing and enjoy enhanced overall health. It is imperative to bear in mind that our lungs are of utmost importance, and thus, it is our responsibility to prioritise their care.
You can get in touch with our respiratory health specialists to understand your health needs and improve and manage your respiratory health.
Sources:
Spread the love, follow us on our social media channels