


Any discussion of kidney diseases invariably brings in the term dialysis. We all know of someone who has been through dialysis.
But what exactly is dialysis, and how does it work?
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve deep into the world of kidney dialysis and explore various aspects associated with it.
Before diving into the details of dialysis, it is important to understand the vital role kidneys play in our bodies:
The kidneys are bean-shaped organs, each roughly the size of a fist, located near the lower back. They perform several essential functions, including:
Unfortunately, due to various factors such as high blood pressure, diabetes, or certain medical conditions, the kidneys can lose their functionality, leading to kidney failure. When the kidneys can no longer effectively perform their tasks, dangerous levels of waste and fluid can build up in the body, leading to life-threatening complications.
Kidney failure is a severe medical condition that requires intervention to manage waste and fluid buildup in the body. This medical intervention is called dialysis.
There are two main types of dialysis:
Let us take a look at all these in detail:
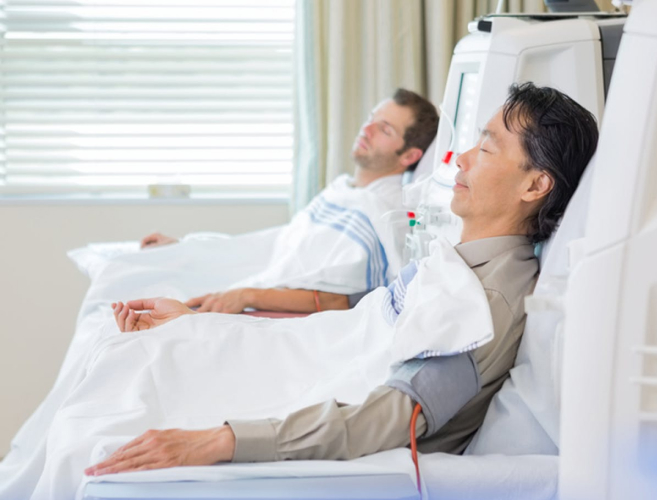

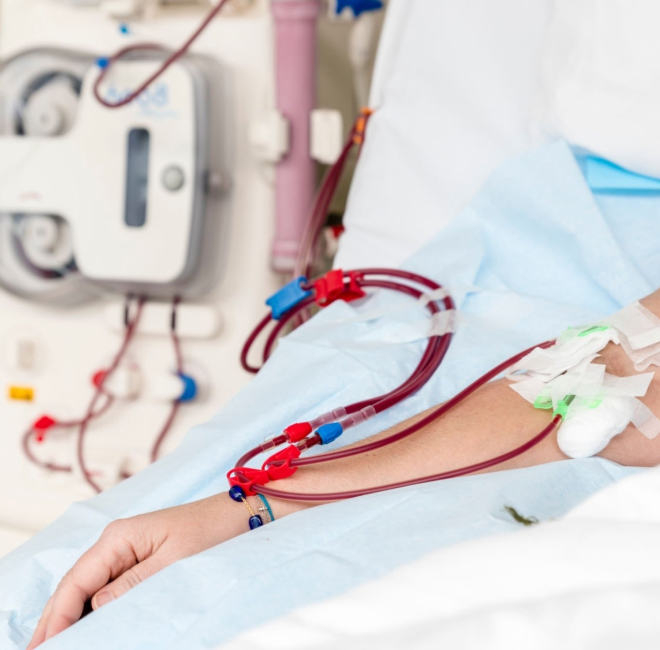
Let’s take a closer look at hemodialysis, as it is the more common type of dialysis.
Hemodialysis typically occurs in a dialysis centre or a hospital. The patient is connected to a hemodialysis machine, which consists of several key components:
During hemodialysis, the patient’s blood is pumped through the dialyser, where it comes into contact with the dialysate solution. Waste products and excess fluids pass through the membrane and are discarded, while clean blood is returned to the patient’s body. Hemodialysis typically takes a few hours and is required multiple times a week.
Hemodialysis is a life-saving procedure, but it does come with its challenges. Patients undergoing hemodialysis often experience changes in their lifestyle, including dietary restrictions and the need to carefully manage their fluid intake. Furthermore, the procedure itself can be physically demanding and may lead to fatigue.
Peritoneal dialysis, while less common than hemodialysis, offers a different approach to managing kidney failure. It can be done at home, providing greater independence to patients.
Peritoneal dialysis uses the peritoneum, a natural membrane in the abdominal cavity, as the filter. Here’s how the process works:
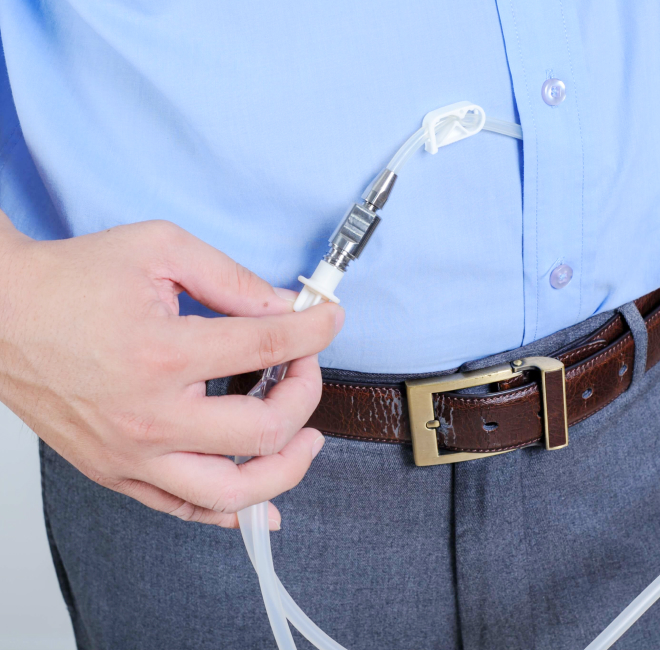

Peritoneal dialysis offers several advantages, such as greater flexibility in treatment location, less dietary restriction, and a gentler impact on the patient’s body. However, it requires strict adherence to the treatment schedule and increased personal responsibility.
Dialysis can be a prolonged process, typically requiring several rounds depending on the condition of the kidney. Living with dialysis can be challenging, but it is essential to understand that life doesn’t end with a diagnosis of kidney failure. With the right support and attitude, many individuals lead fulfilling lives while undergoing dialysis treatment.
Here are some key considerations for maintaining a healthy lifestyle:
Maintaining a kidney-friendly diet is crucial for individuals undergoing dialysis. Such a diet can help manage the buildup of waste and fluid in the body, control blood pressure, and reduce the risk of complications.
Intake of certain foods will be restricted during a kidney disease, such as:
Now let us take a look at some of the dietary recommendations suitable for dialysis patients:
Emotional support and coping strategies are vital for patients undergoing dialysis, as managing a chronic health condition like kidney failure can be mentally and emotionally challenging.
Here are some helpful ways to cope and seek emotional support during your dialysis journey:
Dialysis is a lifeline for individuals suffering from kidney failure. Understanding the basics of this essential medical procedure is crucial for patients, their families, and anyone interested in kidney health. While living with kidney failure and undergoing dialysis can be challenging, it is possible to lead a fulfilling life with the right support and a positive outlook. As medical science continues to advance, we can hope for better, more convenient, and more effective treatments for kidney disease in the future.
People who have the most severe degree of kidney failure, termed stage 5, are generally the ones who need dialysis.
Dialysis may cause pain or discomfort at times, but don’t get discouraged. Some practices can help you avoid or relieve pain and feel better.
Patients often feel fatigued and may experience a drop in blood pressure immediately after dialysis.
Spread the love, follow us on our social media channels