



The human body is a marvel of intricate systems working in harmony, and hormones play a pivotal role in maintaining this delicate balance. Whether you’re a teenager experiencing the first surge of puberty or an adult navigating the challenges of stress and mood swings, understanding hormones is key to unlocking the mysteries of your body and mind.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the fascinating world of hormones, exploring their functions, sources, and the profound impact they have on our physical and emotional well-being.
To embark on our journey through the realm of hormones, we first need to understand what they are. Hormones are chemical messengers produced by various glands in the endocrine system, travelling through the bloodstream to target organs and tissues.
These messengers regulate a multitude of physiological processes, including metabolism, growth, mood, and reproductive functions.
The human body is made up of a complex network of systems that work together to keep us healthy. The endocrine system is like a command centre that controls the release of hormones, which are chemical messengers that regulate various bodily functions.
This system is essential for maintaining balance and coordinating the body’s processes.
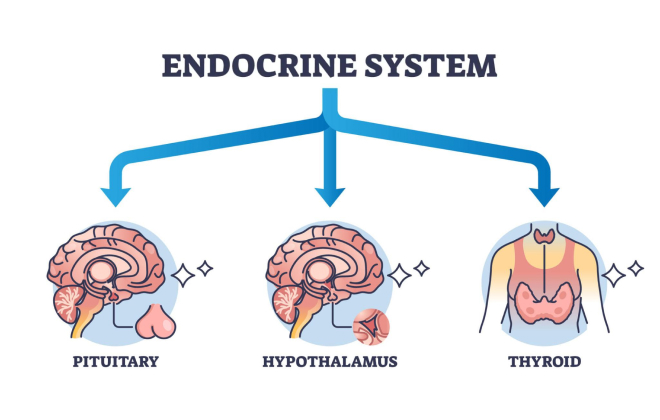
The pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, pancreas, and reproductive glands all play important roles in regulating hormones and functions in the body. The pituitary gland controls other endocrine glands, the thyroid gland regulates metabolism, the adrenal glands respond to stress, the pancreas helps regulate sugar levels, and the reproductive glands produce hormones important for reproduction.
Puberty marks a significant hormonal milestone in an individual’s life, ushering in a period of profound physical and emotional changes. This transformative journey is orchestrated by a surge of hormones, shaping the transition from childhood to adulthood and laying the foundation for the development of secondary sexual characteristics.
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) is released at puberty, signalling the production of LH and FSH by the pituitary gland. These hormones then stimulate testosterone production in males and egg maturation in females. Testosterone and oestrogen drive secondary characteristic development in males and females.

Hormones keep playing a pivotal role even after puberty and continue lifelong.
Stress is common in modern life and triggers the hormone cortisol, which helps the body respond to challenges and daily stressors.
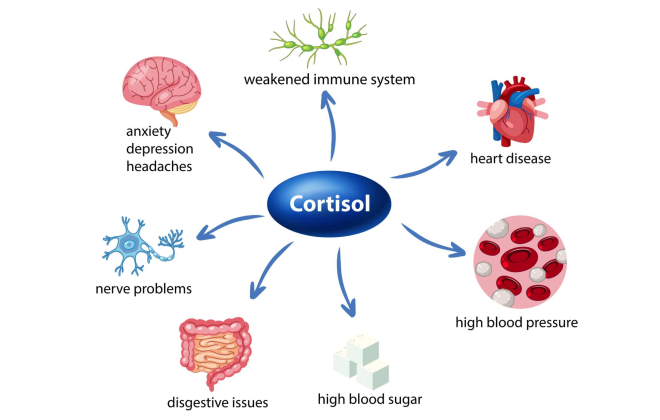
When the body is faced with a threat or stress, it triggers the fight-or-flight response by releasing cortisol. This hormone mobilises energy reserves by breaking down glycogen into glucose for quick energy. Cortisol also suppresses non-essential functions like the immune system and regulates sugar levels by increasing glucose production in the liver to provide energy for the body’s heightened demands during stress.
Chronic stress can lead to high levels of cortisol, which can have negative impacts on immune function, metabolism, cardiovascular health, and mental health. This can lead to increased susceptibility to:
Engaging in relaxation activities like meditation, deep breathing, and mindfulness can lower stress and cortisol levels. Regular exercise is also effective in reducing cortisol levels and promoting overall well-being. Quality sleep is crucial for maintaining a healthy hormonal balance. Establishing consistent sleep patterns and ensuring adequate rest supports cortisol regulation. Adopting a balanced lifestyle with a nutritious diet, social connections, and time for hobbies can increase overall stress resilience.
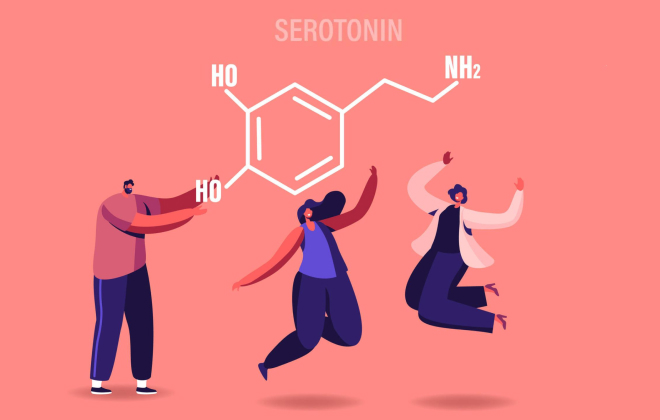
Serotonin is a hormone that plays a crucial role in regulating mood and emotional well-being.
It is often referred to as the “feel-good hormone” because it influences mental health, happiness, stability, and emotional balance. Its functions, sources, and impact on our daily lives are important to understand.
The thyroid gland in the neck controls metabolism and regulates energy production and growth in the body. It plays a crucial role in balancing physiological processes, and keeping it healthy is important for overall well-being.
Our thyroid gland produces two hormones, thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). T3 is the more active form and both are important for regulating metabolism.
The thyroid gland releases calcitonin, a hormone that helps regulate calcium levels in the body and works against parathyroid hormone to maintain bone health.

This beginner’s guide explores the complex world of hormones, highlighting the importance of balance for overall well-being.
By understanding your body and recognising hormonal imbalances, you can work towards achieving hormonal harmony for a healthier and more informed you.
Sources:
Spread the love, follow us on our social media channels