


Did you know globally 17.9 million people lose their lives due to cardiovascular ailments, making it the leading cause of death around the world? Hence an understanding of cardiovascular risk factors is important for preventing and managing heart health.
Recognising risk factors for cardiovascular diseases such as high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle helps identify individuals who are prone to developing these conditions. This knowledge is crucial for both healthcare professionals as well as individuals
The impact of cardiovascular diseases can be lessened by addressing controllable risk factors through lifestyle changes and medical interventions. Educating people about these risk factors is an important aspect of public health initiatives of governments around the world.
Heart diseases can be life-threatening conditions. Therefore, the first stage to ensuring good heart health is to gain knowledge of the common risk factors.
Several well-established risk factors increase the likelihood of developing heart disease.
Considering these key factors helps in assessing patients’ risk profiles and implementing appropriate interventions like adopting a healthy lifestyle or prescribing medications.
Genetic factors have been found to play a significant role in the development of various heart-related conditions, such as hypertension, coronary artery disease, and inherited cardiomyopathies.
Studying an individual’s genetic makeup can help identify specific gene variations that may cause high cholesterol levels, abnormal blood clotting, or structural abnormalities in the heart muscle. This knowledge allows doctors to screen for these issues, accurately predict outcomes, and provide personalised treatments to minimise genetic risks.
Additionally, understanding the genetics of heart diseases opens up possibilities for new treatments such as gene therapies and precision medicine. Ultimately, this understanding can improve early detection and intervention efforts and enhance patient care outcomes in cardiovascular medicine.


Lifestyle choices play a major role in cardiovascular health. Poor habits such as inactivity, unhealthy eating, smoking, and excessive alcohol use increase the risk of heart disease. Regular exercise reduces blood pressure and improves the conditions of blood vessels.
A heart-healthy diet, focusing on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy products while avoiding saturated fats, sodium, added sugars, and processed foods, lowers cholesterol and prevents artery blockage.
Quitting smoking is important as it damages blood vessels and increases clotting. Excessive alcohol raises blood pressure, contributes to obesity, and causes irregular heart rhythms. Changing these behaviours not only benefits the heart but also prevents obesity and diabetes. Healthcare professionals should educate patients on making positive choices for lifelong cardiovascular health.
High pressure can lead to increased stress levels, decreased productivity, and even physical and mental health issues among individuals. To effectively handle this risk factor, professionals need to identify the signs of high pressure in both themselves and their team members. This can be done through monitoring behaviour changes, such as increased irritability or frequent absences due to illness.
This may include implementing strategies such as setting realistic goals, creating a supportive work culture that encourages open communication and teamwork, providing stress management resources, and offering opportunities for relaxation or personal development activities. By addressing high pressure as a risk factor proactively, professionals can create a healthier work environment that promotes overall well-being and productivity.

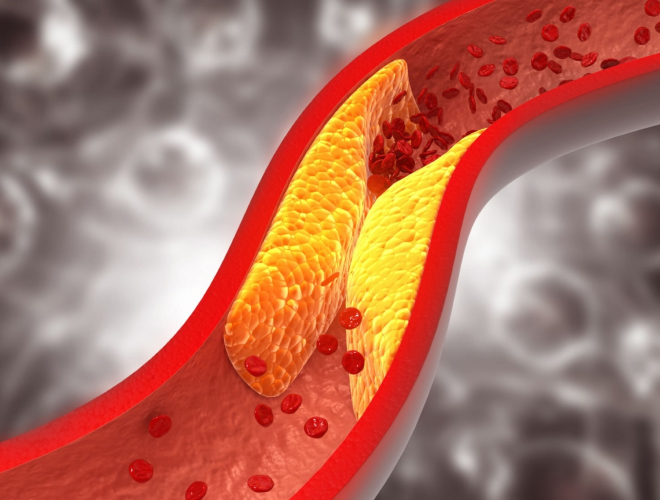
The link between cholesterol levels and risk of heart-related ailments is a well-established and extensively researched area of medical science.
Cholesterol, a waxy substance found in the blood, plays a crucial role in various physiological processes. However, when cholesterol levels are abnormally high, it can lead to the formation of plaque within the arteries, a condition known as atherosclerosis. Over time, this build-up narrows the arteries, compromising proper blood flow and increasing the risk of heart disease. Multiple studies have shown that elevated levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, also known as “bad” cholesterol, contribute significantly to heart disease development.
Conversely, higher levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, commonly referred to as “good” cholesterol, have been associated with reduced risk. Regular monitoring and management of cholesterol levels through lifestyle modifications (such as healthy diet choices) and medications can play an instrumental role in reducing heart disease risk among individuals prone to these conditions.
Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder characterised by high glucose levels. It is a major contributor to cardiovascular problems. People with diabetes are two to three times more likely to develop heart diseases compared to those without. The increased risk is due to several factors: insulin resistance and impaired glucose metabolism lead to fatty deposits in blood vessels, which narrow and block blood flow to vital organs like the heart.
Persistent high blood sugar levels also cause inflammation and damage to the inner lining of blood vessels. It can also lead to oxidative stress, which promotes the buildup of plaque and damages arteries. Additionally, diabetes often coexists with other risk factors for heart disease such as high cholesterol, hypertension, and obesity.
Individuals with diabetes are at risk of various heart-related conditions such as angina, heart attacks, reduced blood flow in the extremities, and strokes. Healthcare professionals should acknowledge diabetes as a major contributor to these cardiovascular issues and prioritise managing both blood sugar levels and reducing the risk of heart problems.
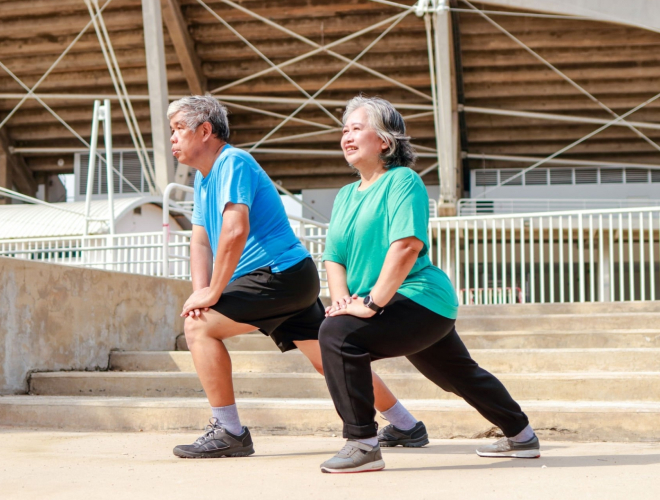

Regular exercise plays a vital role in preventing heart problems and is of utmost importance in maintaining cardiovascular health. Engaging in physical activity consistently helps to strengthen the heart and improve its efficiency, thereby reducing the risk of developing various cardiac conditions.
Exercise assists in regulating blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and body weight, all of which are significant contributors to heart diseases.
Regular exercise is important for managing stress and reducing inflammation in the body, which are closely linked to heart problems. Individuals who incorporate exercise into their everyday routine not only show improved heart function, but also enjoy increased energy levels, improved overall well-being, reduced likelihood of obesity or diabetes, and ultimately a longer lifespan.
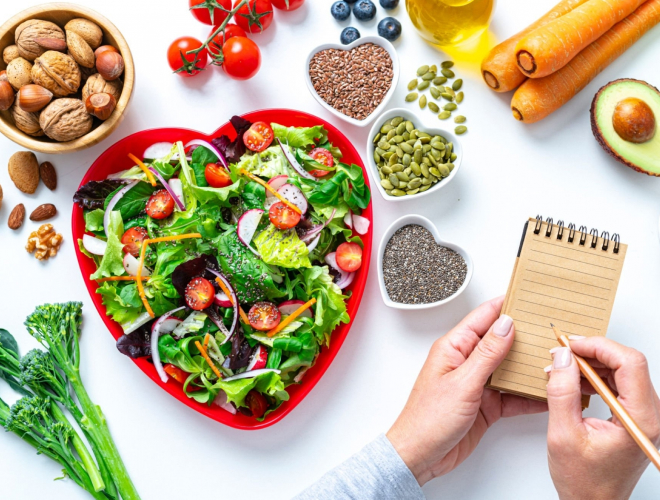
A healthy diet is crucial for heart health and preventing cardiovascular diseases. These guidelines are based on research and expert advice, providing evidence-based recommendations to lower risk factors. The focus lies in maintaining a well-rounded diet with nutrient-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats while limiting saturated and trans fats, added sugars, sodium, and cholesterol. It is also important to maintain a moderate calorie intake and engage in regular physical activity. By following these guidelines and making lifestyle changes, individuals can actively manage their cardiovascular health, potentially preventing or delaying conditions such as hypertension, high cholesterol, and obesity, thus reducing the overall risk of heart disease.
Monitoring and controlling alcohol consumption is also essential for maintaining heart health. Start by setting appropriate limits for yourself based on guidelines provided by reputable health organisations. It is generally recommended that men should not consume more than two standard drinks per day, while women should limit their intake to one drink. Establishing a support system or confiding in trusted friends or family members can help maintain accountability. Regularly assessing the effects of alcohol on your heart health through discussions with a healthcare professional will also aid in monitoring and controlling consumption to protect your cardiovascular well-being.
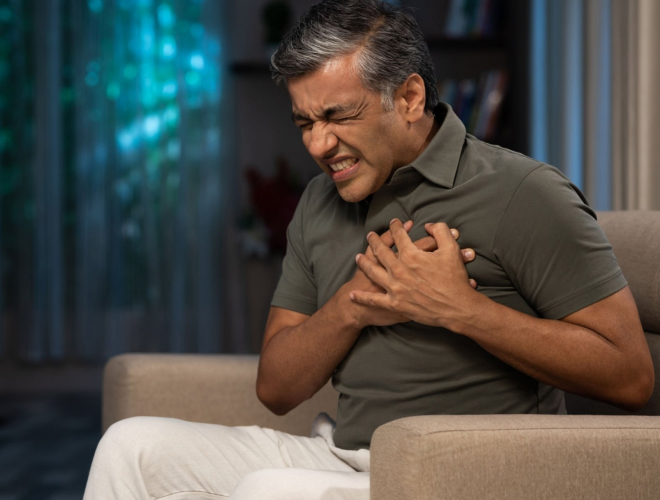


Recognising the signs and symptoms of a heart attack is essential for seeking immediate medical attention and potentially saving a life. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort, which may feel like pressure, squeezing, fullness, or pain that radiates down the arm, jaw, back, or neck.
However, not all heart attacks present with chest pain. Some individuals may experience atypical symptoms such as shortness of breath, nausea or vomiting, lightheadedness or dizziness, cold sweat, fatigue or weakness.
It is important to note that these symptoms can vary between men and women. Men tend to experience classic chest pain while women may have subtle symptoms such as unusual fatigue or sleep disturbances. Professionals in healthcare must be well-versed in recognising these signs and symptoms as prompt diagnosis leads to timely intervention which can significantly improve patient outcomes and reduce morbidity and mortality associated with heart attacks.
When it comes to cardiovascular issues, seeking timely medical help and exploring treatment options is essential for optimal health outcomes. A proactive approach is crucial in identifying and managing conditions such as heart disease, high blood pressure, or arrhythmias.
Consulting a healthcare professional who specialises in cardiology is highly recommended, as they possess the expertise and knowledge necessary to diagnose and create personalised treatment plans. These medical professionals can conduct various diagnostic tests such as electrocardiograms, echocardiograms, or stress tests to assess the severity of the cardiac condition accurately. From there, a range of treatment options can be explored depending on the individual’s specific needs. This may include lifestyle modifications (such as diet changes and exercise), medication therapies (such as statins or beta-blockers), or more invasive interventions (like angioplasty or surgery) if necessary.
Seeking medical help promptly allows for effective management of cardiovascular issues, reducing the risk of complications and improving overall heart health.
Maintaining long-term heart health and preventing complications is important to live a healthy and fulfilling life.
Taking proactive steps towards a healthier heart is an essential component of maintaining overall well-being. By adopting healthy lifestyle choices you can significantly reduce the risk of developing heart diseases.
Additionally, incorporating cardiovascular exercises into your daily routine can help strengthen the heart muscle, improve blood circulation and lower blood pressure.
Educating yourself on the importance of early detection by scheduling regular cheque-ups with healthcare professionals and monitoring cholesterol levels is also an important part of maintaining heart health.
It is worth emphasising that prevention is key when it comes to cardiovascular health; therefore, investing time and effort into cultivating a heart-healthy lifestyle will undoubtedly yield long-term benefits for both physical and mental well-being.
Spread the love, follow us on our social media channels