

Rheumatologic diseases, a broad spectrum of conditions affecting joints, muscles, and connective tissues, often lead to pain, stiffness, and decreased function. While medical management is crucial in addressing the underlying pathology, physical therapy and rehabilitation are integral to optimising patients’ functional abilities and overall well-being. This approach focuses on mitigating the impact of these conditions on daily life, promoting mobility, and empowering individuals to manage their symptoms effectively. By employing a combination of targeted rheumatoid arthritis physiotherapy exercises, manual therapy, and patient education, the medical team aims to restore movement, reduce pain, and enhance the quality of life for those affected by rheumatologic conditions.
Physical therapy and rehabilitation are widely utilised in Malaysia for the management of rheumatic diseases like Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA). These therapies are key components of treatment plans, aimed at improving joint function, reducing pain and fatigue, and enhancing overall quality of life.
Physical therapy (or Physiotherapy) and rehabilitation are essential in rheumatologic care, with several key goals focused on enhancing patients’ lives. A primary objective is pain management, using various techniques to lessen discomfort and reduce dependence on medication.
Improving joint function and mobility is another central goal, achieved through specific exercises and manual therapy to increase the range of motion and decrease stiffness. These interventions also contribute to enhancing overall quality of life, allowing patients to engage more fully in daily activities and social interactions.
Rheumatoid arthritis physiotherapy treatment also works in conjunction with medical treatment, complementing drug therapies and other treatments to improve patient results. A crucial aspect is patient education and self-management, empowering individuals to understand their condition, adopt healthy lifestyles, and effectively manage their symptoms over the long term. By addressing these key goals, physical therapy and rehabilitation help those with rheumatologic conditions to maintain independence, remain active, and improve their well-being.
Physical therapy and rehabilitation address a wide range of rheumatologic conditions. The most common is osteoarthritis (OA), characterised by the breakdown of joint cartilage and resulting in pain and stiffness, and rheumatoid arthritis (RA), an autoimmune disease that causes inflammation and damage to multiple joints.
Other frequently treated conditions include:
Physical therapists customise interventions to address the specific needs of each condition, intending to alleviate symptoms, improve function, and slow disease progression.
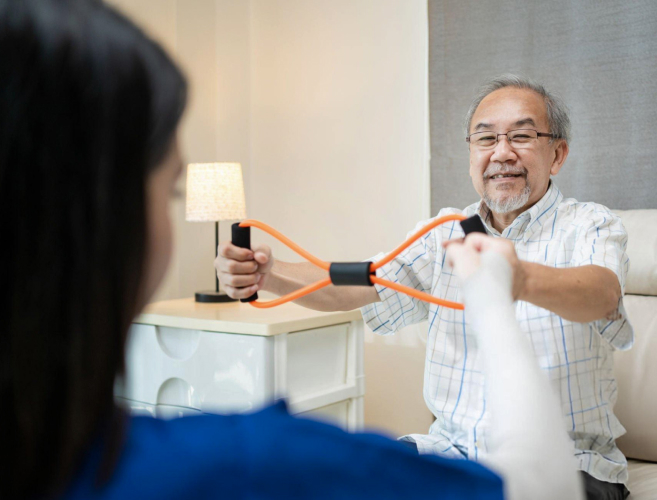

Physiotherapists utilise a variety of interventions to address the diverse needs of patients with rheumatologic conditions. Exercise programs are tailored to improve strength, flexibility, and endurance, while manual therapy techniques such as joint mobilisation and soft tissue mobilisation can help reduce pain and stiffness. Modalities like heat and cold therapy, electrical stimulation, and ultrasound may also be employed to manage pain and inflammation.
Assistive devices, such as braces or splints, may be recommended to support and protect joints, and patients receive education on proper body mechanics and joint protection strategies to minimise stress during daily activities.
The benefits of physiotherapy and rehabilitation in rheumatologic care are wide-ranging, impacting both physical and emotional well-being. These interventions lead to decreased pain and stiffness, along with improved joint function and mobility, enabling patients to perform daily tasks with greater ease. Participation in physical therapy programs can also result in increased strength and endurance, reduced fatigue, and enhanced coordination and balance. Beyond the physical improvements, patients often experience a boost in their overall quality of life, with increased independence, a more positive mood, and greater participation in social and recreational activities.
Pain management is a central component of physiotherapy in rheumatologic care. Physical therapists employ a combination of techniques to alleviate pain, including therapeutic exercises that improve joint movement and reduce stiffness. Manual therapy, such as joint and soft tissue mobilisation, can also be effective in reducing pain. Modalities like heat and cold therapy, electrical stimulation, and ultrasound are often used to modulate pain signals and promote tissue healing. By addressing pain through these various methods, physical therapy helps patients with rheumatologic conditions experience greater comfort and a reduced reliance on pain medication.
A key goal of physical therapy in rheumatologic care is to enhance joint function and mobility. Therapists design individualised exercise programs that include range-of-motion exercises to reduce stiffness and improve flexibility, as well as strengthening exercises to support and stabilise affected joints. Manual therapy techniques, such as joint mobilisation, are used to improve joint mechanics and reduce restrictions. These interventions, along with patient education on proper body mechanics and joint protection, help to optimise joint function, reduce pain, and improve movement for individuals with rheumatologic conditions.
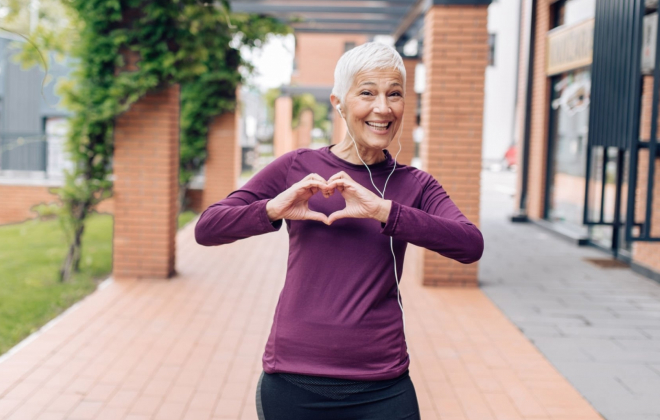

Physical therapy and rehabilitation play a significant role in enhancing the overall quality of life for individuals with rheumatologic conditions. By effectively managing pain and improving joint function and mobility, these interventions enable patients to participate more fully in daily activities, social engagements, and recreational pursuits. Increased independence and a greater ability to perform tasks contribute to a more positive mood, improved self-esteem, and a reduced sense of disability. Physical therapists also provide education and support, empowering patients to take an active role in managing their condition and adopting a healthier lifestyle, further promoting overall well-being.
Patient education and self-management are crucial components of physical therapy in rheumatologic care. Physical therapists empower patients by providing them with the knowledge and skills to understand their condition, manage their symptoms, and make informed decisions about their care. Education encompasses various aspects, including the nature of the disease, proper body mechanics, joint protection strategies, and the importance of exercise and healthy lifestyle habits. Self-management techniques, such as pain management strategies and home exercise programs, enable patients to take an active role in their care, promoting long-term independence and well-being.
While physical therapy offers substantial benefits for rheumatologic conditions, it’s important to acknowledge potential disadvantages. In some cases, particularly during acute flares of inflammation, certain physical therapy interventions might temporarily increase pain or discomfort. There can also be challenges in patient compliance, as adherence to long-term exercise programs can be difficult for some individuals due to time constraints, lack of motivation, or the need for ongoing self-discipline. Additionally, the effectiveness of physical therapy can vary depending on the specific condition, its severity, and individual patient factors, and it may not be effective for all patients.
In conclusion, physical therapy and rehabilitation are indispensable components of rheumatologic care. By addressing pain, improving function, and empowering patients through education, these interventions offer a holistic approach to managing rheumatologic conditions. The emphasis on individualised care, combined with a multidisciplinary approach, ensures that patients receive the support they need to maintain an active and fulfilling life.

Dr Adrian Mark Masnammany
Consultant Physician & Rheumatologist
Spread the love, follow us on our social media channels