

In the world of modern medicine, surgical advancements have paved the way for more effective, less invasive procedures. Among them, arthroscopy has emerged as a groundbreaking technique that has revolutionised the diagnosis and treatment of joint-related conditions. Whether it is arthroscopy knee procedures for sports injuries or arthroscopy shoulder surgery for rotator cuff tears, this minimally invasive method has provided relief to millions of patients worldwide.
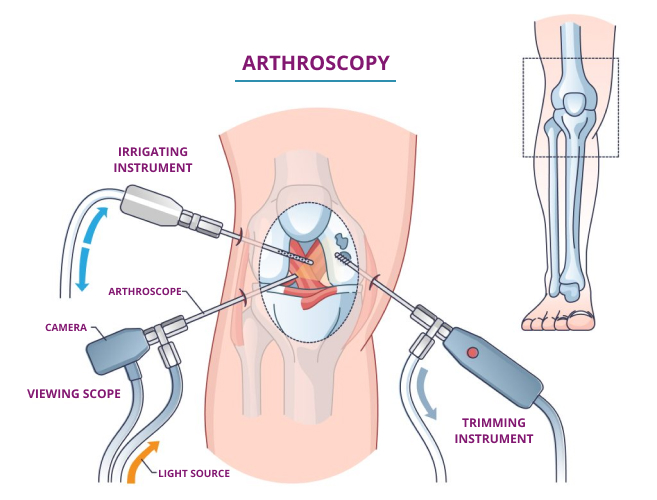
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that allows doctors to examine, diagnose, and treat joint problems using a specialised instrument called an arthroscope.
The arthroscope is a thin, flexible tube with a camera and light source that provides real-time imaging of the joint’s interior.
Arthroscopy uses small incisions to diagnose joint conditions that may not show up on traditional imaging techniques, reducing trauma to surrounding tissues compared to open surgery.
Arthroscopy is used to diagnose and treat a range of joint-related issues. Some of the most common arthroscopy indications include:
Arthroscopy knee procedures are commonly used to treat knee injuries and degenerative conditions. This includes repairing meniscus tears, ACL injuries, cartilage damage, patellar misalignment, and inflammatory conditions such as synovitis. These procedures help improve knee stability, reduce pain, and prevent further joint deterioration.
Arthroscopy shoulder procedures are commonly done to treat conditions such as rotator cuff tears, shoulder impingement syndrome, labral tears, and frozen shoulder. These conditions can cause pain, weakness, mobility issues, and stiffness in the shoulder joint.
Arthroscopy is occasionally used for hip, wrist, and ankle issues such as impingement and tears, ligament injuries, and cartilage damage.
Let’s take a quick peek at the entire procedure.
Before undergoing arthroscopy surgery, you will be evaluated through imaging tests (X-rays, MRI, or CT scans). They are given instructions regarding fasting and medication adjustments.
The procedure follows these steps:
Post-surgery, the patient is monitored in a recovery room before being discharged, usually on the same day for outpatient procedures.
Arthroscopy recovery time varies based on the joint involved, the complexity of the surgery, and the patient’s overall health. Here’s a general timeline:
Pain and swelling can be managed with ice packs and medications. Rest, elevation, and limited weight-bearing activities are recommended. Physical therapy may be started early to prevent stiffness.
Gradual improvement in mobility and function is achieved through strength-building exercises, starting under guidance. Afterwards, individuals can gradually return to light daily activities and desk jobs.
Recovery from sports injuries can take up to 6 months, and it is important to get clearance from a doctor before resuming high-impact activities.
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgery for joint problems, offering benefits over traditional open surgery and is often preferred by patients and surgeons.
Post-surgical rehab and physical therapy are key in helping patients regain strength and function after surgery, aiding in faster recovery.
Arthroscopy is not always necessary for joint problems. It is recommended for those with persistent joint pain that does not improve with conservative treatments, athletes who want quicker recovery, and individuals with specific mechanical joint issues like tears, loose bodies, or impingements.

Arthroscopy has revolutionised orthopaedic surgery with its minimally invasive approach, providing greater precision and faster recovery times. Surgeons use small incisions and a camera-guided system to diagnose and treat joint issues like torn ligaments and cartilage damage, with reduced risk of complications.
Advancing technology makes arthroscopic techniques increasingly sophisticated and versatile, offering more efficient treatment options for orthopaedic conditions. This guide serves as an informative resource on the benefits of arthroscopy for healthcare professionals and patients alike.
Sources:
Spread the love, follow us on our social media channels